
READING SUBTLY
This
was the domain of my Blogger site from 2009 to 2018, when I moved to this domain and started
The Storytelling Ape
. The search option should help you find any of the old posts you're looking for.
How Violent Fiction Works: Rohan Wilson’s “The Roving Party” and James Wood’s Sanguinary Sublime from Conrad to McCarthy
James Wood criticized Cormac McCathy’s “No Country for Old Men” for being too trapped by its own genre tropes. Wood has a strikingly keen eye for literary registers, but he’s missing something crucial in his analysis of McCarthy’s work. Rohan Wilson’s “The Roving Party” works on some of the same principles as McCarthy’s work, and it shows that the authors’ visions extend far beyond the pages of any book.

Any acclaimed novel of violence must be cause for alarm to anyone who believes stories encourage the behaviors depicted in them or contaminate the minds of readers with the attitudes of the characters. “I always read the book as an allegory, as a disguised philosophical argument,” writes David Shields in his widely celebrated manifesto Reality Hunger. Suspicious of any such disguised effort at persuasion, Shields bemoans the continuing popularity of traditional novels and agitates on behalf of a revolutionary new form of writing, a type of collage that is neither marked as fiction nor claimed as truth but functions rather as a happy hybrid—or, depending on your tastes, a careless mess—and is in any case completely lacking in narrative structure. This is because to him giving narrative structure to a piece of writing is itself a rhetorical move. “I always try to read form as content, style as meaning,” Shields writes. “The book is always, in some sense, stutteringly, about its own language” (197).
As arcane as Shields’s approach to reading may sound, his attempt to find some underlying message in every novel resonates with the preoccupations popular among academic literary critics. But what would it mean if novels really were primarily concerned with their own language, as so many students in college literature courses are taught? What if there really were some higher-order meaning we absorbed unconsciously through reading, even as we went about distracting ourselves with the details of description, character, and plot? Might a novel like Heart of Darkness, instead of being about Marlowe’s growing awareness of Kurtz’s descent into inhuman barbarity, really be about something that at first seems merely contextual and incidental, like the darkness—the evil—of sub-Saharan Africa and its inhabitants? Might there be a subtle prompt to regard Kurtz’s transformation as some breed of enlightenment, a fatal lesson encapsulated and propagated by Conrad’s fussy and beautifully tantalizing prose, as if the author were wielding the English language like the fastenings of a yoke over the entire continent?
Novels like Cormac McCarthy’s Blood Meridian and, more recently, Rohan Wilson’s The Roving Party, take place amid a transition from tribal societies to industrial civilization similar to the one occurring in Conrad’s Congo. Is it in this seeming backdrop that we should seek the true meaning of these tales of violence? Both McCarthy’s and Wilson’s novels, it must be noted, represent conspicuous efforts at undermining the sanitized and Manichean myths that arose to justify the displacement and mass killing of indigenous peoples by Europeans as they spread over the far-flung regions of the globe. The white men hunting “Indians” for the bounties on their scalps in Blood Meridian are as beastly and bloodthirsty as the savages peopling the most lurid colonial propaganda, just as the Europeans making up Wilson’s roving party are only distinguishable by the relative degrees of their moral degradation, all of them, including the protagonist, moving in the shadow of their chief quarry, a native Tasmanian chief.
If these novels are about their own language, their form comprising their true content, all in the service of some allegory or argument, then what pleasure would anyone get from them, suggesting as they do that to partake of the fruit of civilization is to become complicit in the original sin of the massacre that made way for it? “There is no document of civilization,” Walter Benjamin wrote, “that is not at the same time a document of barbarism.” It could be that to read these novels is to undergo a sort of rite of expiation, similar to the ritual reenactment of the crucifixion performed by Christians in the lead up to Easter. Alternatively, the real argument hidden in these stories may be still more insidious; what if they’re making the case that violence is both eternal and unavoidable, that it is in our nature to relish it, so there’s no more point in resisting the urge personally than in trying to bring about reform politically?

Shields intimates that the reason we enjoy stories is that they warrant our complacency when he writes, “To ‘tell a story well’ is to make what one writes resemble the schemes people are used to—in other words, their ready-made idea of reality” (200). Just as we take pleasure in arguments for what we already believe, Shields maintains (explicitly) that we delight in stories that depict familiar scenes and resolve in ways compatible with our convictions. And this equating of the pleasure we take in reading with the pleasure we take in having our beliefs reaffirmed is another practice nearly universal among literary critics. Sophisticated readers know better than to conflate the ideas professed by villainous characters like the judge in Blood Meridian with those of the author, but, as one prominent critic complains,
there is often the disquieting sense that McCarthy’s fiction puts certain fond American myths under pressure merely to replace them with one vaster myth—eternal violence, or [Harold] Bloom’s “universal tragedy of blood.” McCarthy’s fiction seems to say, repeatedly, that this is how it has been and how it always will be.
What’s interesting about this interpretation is that it doesn’t come from anyone normally associated with Shields’s school of thought on literature. Indeed, its author, James Wood, is something of a scourge to postmodern scholars of Shields’s ilk.
Wood takes McCarthy to task for his alleged narrative dissemination of the myth of eternal violence in a 2005 New Yorker piece, Red Planet: The Sanguinary Sublime of Cormac McCarthy, a review of his then latest novel No Country for Old Men. Wood too, it turns out, hungers for reality in his novels, and he faults McCarthy’s book for substituting psychological profundity with the pabulum of standard plot devices. He insists that
the book gestures not toward any recognizable reality but merely toward the narrative codes already established by pulp thrillers and action films. The story is itself cinematically familiar. It is 1980, and a young man, Llewelyn Moss, is out antelope hunting in the Texas desert. He stumbles upon several bodies, three trucks, and a case full of money. He takes the money. We know that he is now a marked man; indeed, a killer named Anton Chigurh—it is he who opens the book by strangling the deputy—is on his trail.
Because McCarthy relies on the tropes of a familiar genre to convey his meaning, Wood suggests, that meaning can only apply to the hermetic universe imagined by that genre. In other words, any meaning conveyed in No Country for Old Men is rendered null in transit to the real world.
When Chigurh tells the blameless Carla Jean that “the shape of your path was visible from the beginning,” most readers, tutored in the rhetoric of pulp, will write it off as so much genre guff. But there is a way in which Chigurh is right: the thriller form knew all along that this was her end.
The acuity of Wood’s perception when it comes to the intricacies of literary language is often staggering, and his grasp of how diction and vocabulary provide clues to the narrator’s character and state of mind is equally prodigious. But, in this dismissal of Chigurh as a mere plot contrivance, as in his estimation of No Country for Old Men in general as a “morally empty book,” Wood is quite simply, quite startlingly, mistaken. And we might even say that the critical form knew all along that he would make this mistake.
When Chigurh tells Carla Jean her path was visible, he’s not voicing any hardboiled fatalism, as Wood assumes; he’s pointing out that her predicament came about as a result of a decision her husband Llewelyn Moss made with full knowledge of the promised consequences. And we have to ask, could Wood really have known, before Chigurh showed up at the Moss residence, that Carla Jean would be made to pay for her husband’s defiance? It’s easy enough to point out superficial similarities to genre conventions in the novel (many of which it turns inside-out), but it doesn’t follow that anyone who notices them will be able to foretell how the book will end. Wood, despite his reservations, admits that No Country for Old Men is “very gripping.” But how could it be if the end were so predictable? And, if it were truly so morally empty, why would Wood care how it was going to end enough to be gripped? Indeed, it is in the realm of the characters’ moral natures that Wood is the most blinded by his reliance on critical convention. He argues,
Lewelyn Moss, the hunted, ought not to resemble Anton Chigurh, the hunter, but the flattening effect of the plot makes them essentially indistinguishable. The reader, of course, sides with the hunted. But both have been made unfree by the fake determinism of the thriller.
How could the two men’s fates be determined by the genre if in a good many thrillers the good guy, the hunted, prevails?
One glaring omission in Wood’s analysis is that Moss initially escapes undetected with the drug money he discovers at the scene of the shootout he happens upon while hunting, but he is then tormented by his conscience until he decides to return to the trucks with a jug of water for a dying man who begged him for a drink. “I’m fixin to go do somethin dumbern hell but I’m goin anyways,” he says to Carla Jean when she asks what he’s doing. “If I don’t come back tell Mother I love her” (24). Llewelyn, throughout the ensuing chase, is thus being punished for doing the right thing, an injustice that unsettles readers to the point where we can’t look away—we’re gripped—until we’re assured that he ultimately defeats the agents of that injustice. While Moss risks his life to give a man a drink, Chigurh, as Wood points out, is first seen killing a cop. Moreover, it’s hard to imagine Moss showing up to murder an innocent woman to make good on an ultimatum he’d presented to a man who had already been killed in the interim—as Chigurh does in the scene when he explains to Carla Jean that she’s to be killed because Llewelyn made the wrong choice.
Chigurh is in fact strangely principled, in a morally inverted sort of way, but the claim that he’s indistinguishable from Moss bespeaks a failure of attention completely at odds with the uncannily keen-eyed reading we’ve come to expect from Wood. When he revisits McCarthy’s writing in a review of the 2006 post-apocalyptic novel The Road, collected in the book The Fun Stuff, Wood is once again impressed by McCarthy’s “remarkable effects” but thoroughly baffled by “the matter of his meanings” (61). The novel takes us on a journey south to the sea with a father and his son as they scrounge desperately for food in abandoned houses along the way. Wood credits McCarthy for not substituting allegory for the answer to “a simpler question, more taxing to the imagination and far closer to the primary business of fiction making: what would this world without people look like, feel like?” But then he unaccountably struggles to sift out the novel’s hidden philosophical message. He writes,
A post-apocalyptic vision cannot but provoke dilemmas of theodicy, of the justice of fate; and a lament for the Deus absconditus is both implicit in McCarthy’s imagery—the fine simile of the sun that circles the earth “like a grieving mother with a lamp”—and explicit in his dialogue. Early in the book, the father looks at his son and thinks: “If he is not the word of God God never spoke.” There are thieves and murderers and even cannibals on the loose, and the father and son encounter these fearsome envoys of evil every so often. The son needs to think of himself as “one of the good guys,” and his father assures him that this is the side they are indeed on. (62)
We’re left wondering, is there any way to answer the question of what a post-apocalypse would be like in a story that features starving people reduced to cannibalism without providing fodder for genre-leery critics on the lookout for characters they can reduce to mere “envoys of evil”?

As trenchant as Wood is regarding literary narration, and as erudite—or pedantic, depending on your tastes—as he is regarding theology, the author of the excellent book How Fiction Works can’t help but fall afoul of his own, and his discipline’s, thoroughgoing ignorance when it comes to how plots work, what keeps the moral heart of a story beating. The way Wood fails to account for the forest comprised of the trees he takes such thorough inventory of calls to mind a line of his own from a chapter in The Fun Stuff about Edmund Wilson, describing an uncharacteristic failure on part of this other preeminent critic:
Yet the lack of attention to detail, in a writer whose greatness rests supremely on his use of detail, the unwillingness to talk of fiction as if narrative were a special kind of aesthetic experience and not a reducible proposition… is rather scandalous. (72)
To his credit, though, Wood never writes about novels as if they were completely reducible to their propositions; he doesn’t share David Shields’s conviction that stories are nothing but allegories or disguised philosophical arguments. Indeed, few critics are as eloquent as Wood on the capacity of good narration to communicate the texture of experience in a way all literate people can recognize from their own lived existences.
But Wood isn’t interested in plot. He just doesn’t seem to like them. (There’s no mention of plot in either the table of contents or the index to How Fiction Works.) Worse, he shares Shields’s and other postmodern critics’ impulse to decode plots and their resolutions—though he also searches for ways to reconcile whatever moral he manages to pry from the story with its other elements. This is in fact one of the habits that tends to derail his reviews. Even after lauding The Road’s eschewal of easy allegory in place of the hard work of ground-up realism, Wood can’t help trying to decipher the end of the novel in the context of the religious struggle he sees taking place in it. He writes of the son’s survival,
The boy is indeed a kind of last God, who is “carrying the fire” of belief (the father and son used to speak of themselves, in a kind of familial shorthand, as people who were carrying the fire: it seems to be a version of being “the good guys”.) Since the breath of God passes from man to man, and God cannot die, this boy represents what will survive of humanity, and also points to how life will be rebuilt. (64)
This interpretation underlies Wood’s contemptuous attitude toward other reviewers who found the story uplifting, including Oprah, who used The Road as one of her book club selections. To Wood, the message rings false. He complains that
a paragraph of religious consolation at the end of such a novel is striking, and it throws the book off balance a little, precisely because theology has not seemed exactly central to the book’s inquiry. One has a persistent, uneasy sense that theodicy and the absent God have been merely exploited by the book, engaged with only lightly, without much pressure of interrogation. (64)
Inquiry? Interrogation? Whatever happened to “special kind of aesthetic experience”? Wood first places seemingly inconsequential aspects of the novel at the center of his efforts to read meaning into it, and then he faults the novel for not exploring these aspects at greater length. The more likely conclusion we might draw here is that Wood is simply and woefully mistaken in his interpretation of the book’s meaning. Indeed, Wood’s jump to theology, despite his insistence on its inescapability, is really quite arbitrary, one of countless themes a reader might possibly point to as indicative of the novel’s one true meaning.
Perhaps the problem here is the assumption that a story must have a meaning, some point that can be summed up in a single statement, for it to grip us. Getting beyond the issue of what statement the story is trying to make, we can ask what it is about the aesthetic experience of reading a novel that we find so compelling. For Wood, it’s clear the enjoyment comes from a sort of communion with the narrator, a felt connection forged by language, which effects an estrangement from his own mundane experiences by passing them through the lens of the character’s idiosyncratic vocabulary, phrasings, and metaphors. The sun dimly burning through an overcast sky looks much different after you’ve heard it compared to “a grieving mother with a lamp.” This pleasure in authorial communion and narrative immersion is commonly felt by the more sophisticated of literary readers. But what about less sophisticated readers? Many people who have a hard enough time simply understanding complex sentences, never mind discovering in them clues to the speaker’s personality, nevertheless become absorbed in narratives.
Developmental psychologists Karen Wynn and Paul Bloom, along with then graduate student Kiley Hamlin, serendipitously discovered a major clue to the mystery of why fictional stories engage humans’ intellectual and emotional faculties so powerfully while trying to determine at what age children begin to develop a moral sense. In a series of experiments conducted at the Yale Infant Cognition Center, Wynn and her team found that babies under a year old, even as young as three months, are easily induced to attribute agency to inanimate objects with nothing but a pair of crude eyes to suggest personhood. And, astonishingly, once agency is presumed, these infants begin attending to the behavior of the agents for evidence of their propensities toward being either helpfully social or selfishly aggressive—even when they themselves aren’t the ones to whom the behaviors are directed.
In one of the team’s most dramatic demonstrations, the infants watch puppet shows featuring what Bloom, in his book about the research program Just Babies, refers to as “morality plays” (30). Two rabbits respond to a tiger’s overture of rolling a ball toward them in different ways, one by rolling it back playfully, the other by snatching it up and running away with it. When the babies are offered a choice between the two rabbits after the play, they nearly always reach for the “good guy.” However, other versions of the experiment show that babies do favor aggressive rabbits over nice ones—provided that the victim is itself guilty of some previously witnessed act of selfishness or aggression. So the infants prefer cooperation over selfishness and punishment over complacency.
Wynn and Hamlin didn’t intend to explore the nature of our fascination with fiction, but even the most casual assessment of our most popular stories suggests their appeal to audiences depends on a distinction similar to the one made by the infants in these studies. Indeed, the most basic formula for storytelling could be stated: good guy struggles against bad guy. Our interest is automatically piqued once such a struggle is convincingly presented, and it doesn’t depend on any proposition that can be gleaned from the outcome.
We favor the good guy because his (or her) altruism triggers an emotional response—we like him. And our interest in the ongoing developments of the story—the plot—are both emotional and dynamic. This is what the aesthetic experience of narrative consists of.
The beauty in stories comes from the elevation we get from the experience of witnessing altruism, and the higher the cost to the altruist the more elevating the story. The symmetry of plots is the balance of justice. Stories meant to disturb readers disrupt that balance.The crudest stories pit good guys against bad guys. The more sophisticated stories feature what we hope are good characters struggling against temptations or circumstances that make being good difficult, or downright dangerous. In other words, at the heart of any story is a moral dilemma, a situation in which characters must decide who deserves what fate and what they’re willing to pay to ensure they get it. The specific details of that dilemma are what we recognize as the plot.
The most basic moral, lesson, proposition, or philosophical argument inherent in the experience of attending to a story derives then not from some arbitrary decision on the part of the storyteller but from an injunction encoded in our genome. At some point in human evolution, our ancestor’s survival began to depend on mutual cooperation among all the members of the tribe, and so to this day, and from a startlingly young age, we’re on the lookout for anyone who might be given to exploiting the cooperative norms of our group. Literary critics could charge that the appeal of the altruist is merely another theme we might at this particular moment in history want to elevate to the status of most fundamental aspect of narrative. But I would challenge anyone who believes some other theme, message, or dynamic is more crucial to our engagement with stories to subject their theory to the kind of tests the interplay of selfish and altruistic impulses routinely passes in the Yale studies. Do babies care about theodicy? Are Wynn et al.’s morality plays about their own language?
This isn’t to say that other themes or allegories never play a role in our appreciation of novels. But whatever role they do play is in every case ancillary to the emotional involvement we have with the moral dilemmas of the plot. 1984 and Animal Farm are clear examples of allegories—but their greatness as stories is attributable to the appeal of their characters and the convincing difficulty of their dilemmas. Without a good plot, no one would stick around for the lesson. If we didn’t first believe Winston Smith deserved to escape Room 101 and that Boxer deserved a better fate than the knackery, we’d never subsequently be moved to contemplate the evils of totalitarianism. What makes these such powerful allegories is that, if you subtracted the political message, they’d still be great stories because they engage our moral emotions.
What makes violence so compelling in fiction then is probably not that it sublimates our own violent urges, or that it justifies any civilization’s past crimes; violence simply ups the stakes for the moral dilemmas faced by the characters. The moment by moment drama in The Road, for instance, has nothing to do with whether anyone continues to believe in God. The drama comes from the father and son’s struggles to resist having to succumb to theft and cannibalism to survive. That’s the most obvious theme recurring throughout the novel. And you get the sense that were it not for the boy’s constant pleas for reassurance that they would never kill and eat anyone—the ultimate act of selfish aggression—and that they would never resort to bullying and stealing, the father quite likely would have made use of such expedients. The fire that they’re carrying is not the light of God; it’s the spark of humanity, the refusal to forfeit their human decency. (Wood doesn't catch that the fire was handed off from Sheriff Bell's father at the end of No Country.) The boy may very well be a redeemer, in that he helps his father make it to the end of his life with a clear conscience, but unless you believe morality is exclusively the bailiwick of religion God’s role in the story is marginal at best.
What the critics given to dismissing plots as pointless fabrications fail to consider is that just as idiosyncratic language and simile estranges readers from their mundane existence so too the high-stakes dilemmas that make up plots can make us see our own choices in a different light, effecting their own breed of estrangement with regard to our moral perceptions and habits. In The Roving Party, set in the early nineteenth century, Black Bill, a native Tasmanian raised by a white family, joins a group of men led by a farmer named John Batman to hunt and kill other native Tasmanians and secure the territory for the colonials. The dilemmas Bill faces are like nothing most readers will ever encounter. But their difficulty is nonetheless universally understandable. In the following scene, Bill, who is also called the Vandemonian, along with a young boy and two native scouts, watches as Batman steps up to a wounded clansman in the aftermath of a raid on his people.
Batman considered the silent man secreted there in the hollow and thumbed back the hammers. He put one foot either side of the clansman’s outstretched legs and showed him the long void of those bores, standing thus prepared through a few creakings of the trees. The warrior was wide-eyed, looking to Bill and to the Dharugs.
The eruption raised the birds squealing from the branches. As the gunsmoke cleared the fellow slumped forward and spilled upon the soil a stream of arterial blood. The hollow behind was peppered with pieces of skull and other matter. John Batman snapped open the locks, cleaned out the pans with his cloth and mopped the blood off the barrels. He looked around at the rovers.
The boy was openmouthed, pale, and he stared at the ruination laid out there at his feet and stepped back as the blood ran near his rags. The Dharugs had by now turned away and did not look back. They began retracing their track through the rainforest, picking among the fallen trunks. But Black Bill alone among that party met Batman’s eye. He resettled his fowling piece across his back and spat on the ferns, watching Batman. Batman pulled out his rum, popped loose the cork, and drank. He held out the vessel to Bill. The Vandemonian looked at him. Then he turned to follow the Parramatta men out among the lemon myrtles and antique pines. (92)
If Rohan Wilson had wanted to expound on the evils of colonialism in Tasmania, he might have written about how Batman, a real figure from history, murdered several men he could easily have taken prisoner. But Wilson wanted to tell a story, and he knew that dilemmas like this one would grip our emotions. He likewise knew he didn’t have to explain that Bill, however much he disapproves of the murder, can’t afford to challenge his white benefactor in any less subtle manner than meeting his eyes and refusing his rum.
Unfortunately, Batman registers the subtle rebuke all too readily. Instead of killing a native lawman wounded in a later raid himself, Batman leaves the task to Bill, who this time isn’t allowed the option of silently disapproving. But the way Wilson describes Bill’s actions leaves no doubt in the reader’s mind about his feelings, and those feelings have important consequences for how we feel about the character.
Black Bill removed his hat. He worked back the heavy cocks of both barrels and they settled with a dull clunk. Taralta clutched at his swaddled chest and looked Bill in the eyes, as wordless as ground stone. Bill brought up the massive gun and steadied the barrels across his forearm as his broken fingers could not take the weight. The sight of those octagonal bores levelled on him caused the lawman to huddle down behind his hands and cry out, and Bill steadied the gun but there was no clear shot he might take. He waited.
See now, he said. Move your hands.
The lawman crabbed away over the dirt, still with his arms upraised, and Bill followed him and kicked him in the bandaged ribs and kicked at his arms.
menenger, Bill said, menenger.
The lawman curled up more tightly. Bill brought the heel of his boot to bear on the wounded man but he kicked in vain while Taralta folded his arms ever tighter around his head.
Black Bill lowered the gun. Wattlebirds made their yac-a-yac coughs in the bush behind and he gazed at the blue hills to the south and the snow clouds forming above them. When Bill looked again at the lawman he was watching through his hands, dirt and ash stuck in the cords of his ochred hair. Bill brought the gun up, balanced it across his arm again and tucked the butt into his shoulder. Then he fired into the lawman’s head.
The almighty concussion rattled the wind in his chest and the gun bucked from his grip and fell. He turned away, holding his shoulder. Blood had spattered his face, his arms, the front of his shirt. For a time he would not look at the body of the lawman where it lay near the fire. He rubbed at the bruising on his shoulder; watched storms amass around the southern peaks. After a while he turned to survey the slaughter he had wrought.
One of the lawman’s arms was gone at the elbow and the teeth seated in the jawbone could be seen through the cheek. There was flesh blown every place. He picked up the Manton gun. The locks were soiled and he fingered out the grime, and then with the corner of his coat cleaned the pan and blew into the latchworks. He brought the weapon up to eye level and peered along its sights for barrel warps or any misalignment then, content, slung the leather on his shoulder. Without a rearward glance he stalked off, his hat replaced, his boots slipping in the blood. Smoke from the fire blew around him in a snarl raised on the wind and dispersed again on the same. (102-4)
Depending on their particular ideological bent, critics may charge that a scene like this simply promotes the type of violence it depicts, or that it encourages a negative view of native Tasmanians—or indigenous peoples generally—as of such weak moral fiber that they can be made to turn against their own countrymen. And pointing out that the aspect of the scene that captures our attention is the process, the experience, of witnessing Bill’s struggle to resolve his dilemma would do little to ease their worries; after all, even if the message is ancillary, its influence could still be pernicious.
The reason that critics applying their favored political theories to their analyses of fiction so often stray into the realm of the absurd is that the only readers who experience stories the same way as they do will be the ones who share the same ideological preoccupations. You can turn any novel into a Rorschach, pulling out disparate shapes and elements to blur into some devious message. But any reader approaching the writing without your political theories or your critical approach will likely come away with a much more basic and obvious lesson. Black Bill’s dilemma is that he has to kill many of his fellow Tasmanians if he wants to continue living as part of a community of whites. If readers take on his attitude toward killing as it’s demonstrated in the scene when he kills Taralta, they’ll be more reluctant to do it, not less. Bill clearly loathes what he’s forced to do. And if any race comes out looking bad it’s the whites, since they’re the ones whose culture forces Bill to choose between his family’s well-being and the dictates of his conscience.
Readers likely have little awareness of being influenced by the overarching themes in their favorite stories, but upon reflection the meaning of those themes is usually pretty obvious. Recent research into how reading the Harry Potter books has impacted young people’s political views, for instance, shows that fans of the series are more accepting of out-groups, more tolerant, less predisposed to authoritarianism, more supporting of equality, and more opposed to violence and torture. Anthony Gierzynsky, the author of the study, points out, “As Harry Potter fans will have noted, these are major themes repeated throughout the series.” The messages that reach readers are the conspicuous ones, not the supposedly hidden ones critics pride themselves on being able to suss out.
It’s an interesting question just how wicked stories could persuade us to be, relying as they do on our instinctual moral sense. Fans could perhaps be biased toward evil by themes about the threat posed by some out-group, or the debased nature of the lower orders, or nonbelievers in the accepted deities—since the salience of these concepts likewise seems to be inborn. But stories told from the perspective of someone belonging to the persecuted group could provide an antidote. At any rate, there’s a solid case to be made that novels have helped the moral of arc of history bend toward greater justice and compassion.
Even a novel with violence as pervasive and chaotic as it is in Blood Meridian sets up a moral gradient for the characters to occupy—though finding where the judge fits is a quite complicated endeavor—and the one with the most qualms about killing happens to be the protagonist, referred to simply as the kid. “You alone were mutinous,” the judge says to him. “You alone reserved in your soul some corner of clemency for the heathen” (299). The kid’s character is revealed much the way Black Bill’s is in The Roving Party, as readers witness him working through high-stakes dilemmas. After drawing arrows to determine who in the band of scalp hunters will stay behind to kill some of their wounded (to prevent a worse fate at the hands of the men pursuing them), the kid finds himself tasked with euthanizing a man who would otherwise survive.
You wont thank me if I let you off, he said.
Do it then you son of a bitch.
The kid sat. A light wind was blowing out of the north and some doves had begun to call in the thicket of greasewood behind them.
If you want me just to leave you I will.
Shelby didnt answer
He pushed a furrow in the sand with the heel of his boot. You’ll have to say.
Will you leave me a gun?
You know I can’t leave you no gun.
You’re no better than him. Are you?
The kid didn’t answer. (208)
That “him” is ambiguous; it could either be Glanton, the leader of the gang whose orders the kid is ignoring, or the judge, who engages him throughout the later parts of the novel in a debate about the necessity of violence in history. We know by now that the kid really is better than the judge—at least in the sense that Shelby means. And the kid handles the dilemma, as best he can, by hiding Shelby in some bushes and leaving him with a canteen of water.
These three passages from The Roving Party and Blood Meridian reveal as well something about the language commonly used by authors of violent novels going back to Conrad (perhaps as far back as Tolstoy). Faced with the choice of killing a man—or of standing idly by and allowing him to be killed—the characters hesitate, and the space of their hesitation is filled with details like the type of birdsong that can be heard. This style of “dirty realism,” a turning away from abstraction, away even from thought, to focus intensely on physical objects and the natural world, frustrates critics like James Wood because they prefer their prose to register the characters’ meanderings of mind in the way that only written language can. Writing about No Country for Old Men, Wood complains about all the labeling and descriptions of weapons and vehicles to the exclusion of thought and emotion.
Here is Hemingway’s influence, so popular in male American fiction, of both the pulpy and the highbrow kind. It recalls the language of “A Farewell to Arms”: “He looked very dead. It was raining. I had liked him as well as anyone I ever knew.” What appears to be thought is in fact suppressed thought, the mere ratification of male taciturnity. The attempt to stifle sentimentality—“He looked very dead”—itself comes to seem a sentimental mannerism. McCarthy has never been much interested in consciousness and once declared that as far as he was concerned Henry James wasn’t literature. Alas, his new book, with its gleaming equipment of death, its mindless men and absent (but appropriately sentimentalized) women, its rigid, impacted prose, and its meaningless story, is perhaps the logical result of a literary hostility to Mind.
Here again Wood is relaxing his otherwise razor-keen capacity for gleaning insights from language and relying instead on the anemic conventions of literary criticism—a discipline obsessed with the enactment of gender roles. (I’m sure Suzanne Collins would be amused by this idea of masculine taciturnity.) But Wood is right to recognize the natural tension between a literature of action and a literature of mind. Imagine how much the impact of Black Bill’s struggle with the necessity of killing Taralta would be blunted if we were privy to his thoughts, all of which are implicit in the scene as Wilson has rendered it anyway.
Fascinatingly, though, it seems that Wood eventually realized the actual purpose of this kind of evasive prose—and it was Cormac McCarthy he learned it from. As much as Wood lusts after some leap into theological lucubration as characters reflect on the lessons of the post-apocalypse or the meanings of violence, the psychological reality is that it is often in the midst of violence or when confronted with imminent death that people are least given to introspection. As Wood explains in writing about the prose style of The Road,
McCarthy writes at one point that the father could not tell the son about life before the apocalypse: “He could not construct for the child’s pleasure the world he’d lost without constructing the loss as well and thought perhaps the child had known this better than he.” It is the same for the book’s prose style: just as the father cannot construct a story for the boy without also constructing the loss, so the novelist cannot construct the loss without the ghost of the departed fullness, the world as it once was. (55)
The rituals of weapon reloading, car repair, and wound wrapping that Wood finds so offputtingly affected in No Country for Old Men are precisely the kind of practicalities people would try to engage their minds with in the aftermath of violence to avoid facing the reality. But this linguistic and attentional coping strategy is not without moral implications of its own.
In the opening of The Roving Party, Black Bill receives a visit from some of the very clansmen he’s been asked by John Batman to hunt. The headman of the group is a formidable warrior named Manalargena (another real historical figure), who is said to have magical powers. He has come to recruit Bill to help in fighting against the whites, unaware of Bill’s already settled loyalties. When Bill refuses to come fight with Manalargena, the headman’s response is to tell a story about two brothers who live near a river where they catch plenty of crayfish, make fires, and sing songs. Then someone new arrives on the scene:
Hunter come to the river. He is hungry hunter you see. He want crayfish. He see them brother eating crayfish, singing song. He want crayfish too. He bring up spear. Here the headman made as if to raise something. He bring up that spear and he call out: I hungry, you give me that crayfish. He hold that spear and he call out. But them brother they scared you see. They scared and they run. They run and they change. They change to wallaby and they jump. Now they jump and jump and the hunter he follow them.
So hunter he change too. He run and he change to that wallaby and he jump. Now three wallaby jump near river. They eat grass. They forget crayfish. They eat grass and they drink water and they forget crayfish. Three wallaby near the river. Very big river. (7-8)
Bill initially dismisses the story, saying it makes no sense. Indeed, as a story, it’s terrible. The characters have no substance and the transformation seems morally irrelevant. The story is pure allegory. Interestingly, though, by the end of the novel, its meaning is perfectly clear to Bill. Taking on the roles of hunter and hunted leaves no room for songs, no place for what began the hunt in the first place, creating a life closer to that of animals than of humans. There are no more fires.
Wood counts three registers authors like Conrad and McCarthy—and we can add Wilson—use in their writing. The first is the dirty realism that conveys the characters’ unwillingness to reflect on their circumstances or on the state of their souls. The third is the lofty but oblique discourse on God’s presence or absence in a world of tragedy and carnage Wood finds so ineffectual. For most readers, though, it’s the second register that stands out. Here’s how Wood describes it:
Hard detail and a fine eye is combined with exquisite, gnarled, slightly antique (and even slightly clumsy or heavy) lyricism. It ought not to work, and sometimes it does not. But many of its effects are beautiful—and not only beautiful, but powerfully efficient as poetry. (59)
This description captures what’s both great and frustrating about the best and worst lines in these authors’ novels. But Wood takes the tradition for granted without asking why this haltingly graceful and heavy-handedly subtle language is so well-suited to these violent stories. The writers are compelled to use this kind of language by the very effects of the plot and setting that critics today so often fail to appreciate—though Wood does gesture toward it in the title of his essay on No Country for Old Men. The dream logic of song and simile that goes into the aesthetic experience of bearing witness to the characters sparsely peopling the starkly barren and darkly ominous landscapes of these novels carries within it the breath of the sublime.
In coming to care about characters whose fates unfold in the aftermath of civilization, or in regions where civilization has yet to take hold, places where bloody aggression and violent death are daily concerns and witnessed realities, we’re forced to adjust emotionally to the worlds they inhabit. Experiencing a single death brings a sense of tragedy, but coming to grips with a thousand deaths has a more curious effect. And it is this effect that the strange tangles of metaphorical prose both gesture toward and help to induce. The sheer immensity of the loss, the casual brushing away of so many bodies and the blotting out of so much unique consciousness, overstresses the capacity of any individual to comprehend it. The result is paradoxical, a fixation on the material objects still remaining, and a sliding off of one’s mind onto a plane of mental existence where the material has scarcely any reality at all because it has scarcely any significance at all. The move toward the sublime is a lifting up toward infinite abstraction, the most distant perspective ever possible on the universe, where every image is a symbol for some essence, where every embrace is a symbol for human connectedness, where every individual human is a symbol for humanity. This isn’t the abstraction of logic, the working out of implications about God or cosmic origins. It’s the abstraction of the dream or the religious experience, an encounter with the sacred and the eternal, a falling and fading away of the world of the material and the particular and the mundane.
The prevailing assumption among critics and readers alike is that fiction, especially literary fiction, attempts to represent some facet of life, so the nature of a given representation can be interpreted as a comment on whatever is being represented. But what if the representations, the correspondences between the fictional world and the nonfictional one, merely serve to make the story more convincing, more worthy of our precious attention? What if fiction isn’t meant to represent reality so much as to alter our perceptions of it? Critics can fault plots like the one in No Country for Old Men, and characters like Anton Chigurh, for having no counterparts outside the world of the story, mooting any comment about the real world the book may be trying to make. But what if the purpose of drawing readers into fictional worlds is to help them see their own worlds anew by giving them a taste of what it would be like to live a much different existence? Even the novels that hew more closely to the mundane, the unremarkable passage of time, are condensed versions of the characters’ lives, encouraging readers to take a broader perspective on their own. The criteria we should apply to our assessments of novels then would not be how well they represent reality and how accurate or laudable their commentaries are. We should instead judge novels by how effectively they pull us into the worlds they create for themselves and how differently we look at our own world in the wake of the experience. And since high-stakes moral dilemmas are the heart of stories we might wonder what effect the experience of witnessing them will have on our own lower-stakes lives.
Also read:
HUNGER GAME THEORY: Post-Apocalyptic Fiction and the Rebirth of Humanity
Life's White Machine: James Wood and What Doesn't Happen in Fiction
LET'S PLAY KILL YOUR BROTHER: FICTION AS A MORAL DILEMMA GAME
HUNGER GAME THEORY: Post-Apocalyptic Fiction and the Rebirth of Humanity
We can’t help feeling strong positive emotions toward altruists. Katniss wins over readers and viewers the moment she volunteers to serve as tribute in place of her younger sister, whose name was picked in the lottery. What’s interesting, though, is that at several points in the story Katniss actually does engage in purely rational strategizing. She doesn’t attempt to help Peeta for a long time after she finds out he’s been wounded trying to protect her—why would she when they’re only going to have to fight each other in later rounds?
The appeal of post-apocalyptic stories stems from the joy of experiencing anew the birth of humanity. The renaissance never occurs in M.T. Anderson’s Feed, in which the main character is rendered hopelessly complacent by the entertainment and advertising beamed directly into his brain. And it is that very complacency, the product of our modern civilization's unfathomable complexity, that most threatens our sense of our own humanity. There was likely a time, though, when small groups composed of members of our species were beset by outside groups composed of individuals of a different nature, a nature that when juxtaposed with ours left no doubt as to who the humans were.
In Suzanne Collins’ The Hunger Games, Katniss Everdeen reflects on how the life-or-death stakes of the contest she and her fellow “tributes” are made to participate in can transform teenage boys and girls into crazed killers. She’s been brought to a high-tech mega-city from District 12, a mining town as quaint as the so-called Capitol is futuristic. Peeta Mellark, who was chosen by lottery as the other half of the boy-girl pair of tributes from the district, has just said to her, “I want to die as myself…I don’t want them to change me in there. Turn me into some kind of monster that I’m not.” Peeta also wants “to show the Capitol they don’t own me. That I’m more than just a piece in their Games.” The idea startles Katniss, who at this point is thinking of nothing but surviving the games—knowing full well that there are twenty-two more tributes and only one will be allowed to leave the arena alive. Annoyed by Peeta’s pronouncement of a higher purpose, she thinks,
We will see how high and mighty he is when he’s faced with life and death. He’ll probably turn into one of those raging beast tributes, the kind who tries to eat someone’s heart after they’ve killed them. There was a guy like that a few years ago from District 6 called Titus. He went completely savage and the Gamemakers had to have him stunned with electric guns to collect the bodies of the players he’d killed before he ate them. There are no rules in the arena, but cannibalism doesn’t play well with the Capitol audience, so they tried to head it off. (141-3)
Cannibalism is the ultimate relinquishing of the mantle of humanity because it entails denying the humanity of those being hunted for food. It’s the most basic form of selfishness: I kill you so I can live.
The threat posed to humanity by hunger is also the main theme of Cormac McCarthy’s The Road, the story of a father and son wandering around the ruins of a collapsed civilization. The two routinely search abandoned houses for food and supplies, and in one they discover a bunch of people locked in a cellar. The gruesome clue to the mystery of why they’re being kept is that some have limbs amputated. The men keeping them are devouring the living bodies a piece at a time. After a harrowing escape, the boy, understandably disturbed, asks, “They’re going to kill those people, arent they?” His father, trying to protect him from the harsh reality, answers yes, but tries to be evasive, leading to this exchange:
Why do they have to do that?
I dont know.
Are they going to eat them?
I dont know.
They’re going to eat them, arent they?
Yes.
And we couldnt help them because then they’d eat us too.
Yes.
And that’s why we couldnt help them.
Yes.
Okay.
But of course it’s not okay. After they’ve put some more distance between them and the human abattoir, the boy starts to cry. His father presses him to explain what’s wrong:
Just tell me.
We wouldnt ever eat anybody, would we?
No. Of course not.
Even if we were starving?
We’re starving now.
You said we werent.
I said we werent dying. I didn’t say we werent starving.
But we wouldnt.
No. We wouldnt.
No matter what.
No. No matter what.
Because we’re the good guys.
Yes.
And we’re carrying the fire.
And we’re carrying the fire. Yes.
Okay. (127-9)
And this time it actually is okay because the boy, like Peeta Mellark, has made it clear that if the choice is between dying and becoming a monster he wants to die.
This preference for death over depredation of others is one of the hallmarks of humanity, and it poses a major difficulty for economists and evolutionary biologists alike. How could this type of selflessness possibly evolve?
John von Neumann, one of the founders of game theory, served an important role in developing the policies that have so far prevented the real life apocalypse from taking place. He is credited with the strategy of Mutually Assured Destruction, or MAD (he liked amusing acronyms), that prevailed during the Cold War. As the name implies, the goal was to assure the Soviets that if they attacked us everyone would die. Since the U.S. knew the same was true of any of our own plans to attack the Soviets, a tense peace, or Cold War, was the inevitable result. But von Neumann was not at all content with this peace. He devoted his twilight years to pushing for the development of Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles (ICBMs) that would allow the U.S. to bomb Russia without giving the Soviets a chance to respond. In 1950, he made the infamous remark that inspired Dr. Strangelove: “If you say why not bomb them tomorrow, I say, why not today. If you say today at five o’clock, I say why not one o’clock?”
Von Neumann’s eagerness to hit the Russians first was based on the logic of game theory, and that same logic is at play in The Hunger Games and other post-apocalyptic fiction. The problem with cooperation, whether between rival nations or between individual competitors in a game of life-or-death, is that it requires trust—and once one player begins to trust the other he or see becomes vulnerable to exploitation, the proverbial stab in the back from the person who’s supposed to be watching it. Game theorists model this dynamic with a thought experiment called the Prisoner’s Dilemma. Imagine two criminals are captured and taken to separate interrogation rooms. Each criminal has the option of either cooperating with the other criminal by remaining silent or betraying him or her by confessing. Here’s a graph of the possible outcomes:
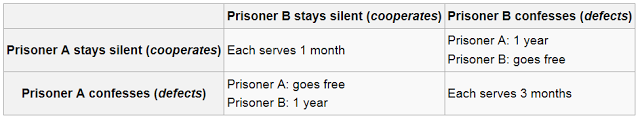
No matter what the other player does, each of them achieves a better outcome by confessing. Von Neumann saw the standoff between the U.S. and the Soviets as a Prisoner’s Dilemma; by not launching nukes, each side was cooperating with the other. Eventually, though, one of them had to realize that the only rational thing to do was be the first to defect.
But the way humans play games is a bit different. As it turned out, von Neumann was wrong about the game theory implications of the Cold War—neither side ever did pull the trigger; both prisoners kept their mouth shut. In Collins' novel, Katniss faces a Prisoner's Dilemma every time she encounters another tribute who may be willing to team up with her in the hunger game. The graph for her and Peeta looks like this:
In the context of the hunger games, then, it makes sense to team up with rivals as long as they have useful skills, knowledge, or strength. Each tribute knows, furthermore, that as long as he or she is useful to a teammate, it would be irrational for that teammate to defect.
The Prisoner’s Dilemma logic gets much more complicated when you start having players try to solve it over multiple rounds of play. Game theorists refer to each time a player has to make a choice as an iteration. And to model human cooperative behavior you have to not only have multiple iterations but also find a way to factor in each player’s awareness of how rivals have responded to the dilemma in the past. Humans have reputations. Katniss, for instance, doesn’t trust the Career tributes because they have a reputation for being ruthless. She even begins to suspect Peeta when she sees that he’s teamed up with the Careers. (His knowledge of Katniss is a resource to them, but he’s using that knowledge in an irrational way—to protect her instead of himself.) On the other hand, Katniss trusts Rue because she's young and dependent—and because she comes from an adjacent district not known for sending tributes who are cold-blooded.
When you have multiple iterations and reputations, you also open the door for punishments and rewards. At the most basic level, people reward those who they witness cooperating by being more willing to cooperate with them. As we read or watch The Hunger Games, we can actually experience the emotional shift that occurs in ourselves as we witness Katniss’s cooperative behavior.
People punish those who defect by being especially reluctant to trust them. At this point, the analysis is still within the realm of the purely selfish and rational. But you can’t stay in that realm for very long when you’re talking about the ways humans respond to one another.
Each time Katniss encounters another tribute in the games she faces a Prisoner’s Dilemma. Until the final round, the hunger games are not a zero-sum contest—which means that a gain for one doesn’t necessarily mean a loss for the other. Ultimately, of course, Katniss and Peeta are playing a zero-sum game; since only one tribute can win, one of any two surviving players at the end will have to kill the other (or let him die). Every time one tribute kills another, the math of the Prisoner’s Dilemma has to be adjusted. Peeta, for instance, wouldn’t want to betray Katniss early on, while there are still several tributes trying to kill them, but he would want to balance the benefits of her resources with whatever advantage he could gain from her unsuspecting trust—so as they approach the last few tributes, his temptation to betray her gets stronger. Of course, Katniss knows this too, and so the same logic applies for her.
As everyone who’s read the novel or seen the movie knows, however, this isn’t how either Peeta or Katniss plays in the hunger games. And we already have an idea of why that is: Peeta has said he doesn’t want to let the games turn him into a monster. Figuring out the calculus of the most rational decisions is well and good, but humans are often moved by their emotions—fear, affection, guilt, indebtedness, love, rage—to behave in ways that are completely irrational—at least in the near term. Peeta is in love with Katniss, and though she doesn’t really quite trust him at first, she proves willing to sacrifice herself in order to help him survive. This goes well beyond cooperation to serve purely selfish interests.

Many evolutionary theorists believe that at some point in our evolutionary history, humans began competing with each other to see who could be the most cooperative. This paradoxical idea emerges out of a type of interaction between and among individuals called costly signaling. Many social creatures must decide who among their conspecifics would make the best allies. And all sexually reproducing animals have to have some way to decide with whom to mate. Determining who would make the best ally or who would be the fittest mate is so important that only the most reliable signals are given any heed. What makes the signals reliable is their cost—only the fittest can afford to engage in costly signaling. Some animals have elaborate feathers that are conspicuous to predators; others have massive antlers. This is known as the handicap principle. In humans, the theory goes, altruism somehow emerged as a costly signal, so that the fittest demonstrate their fitness by engaging in behaviors that benefit others to their own detriment. The boy in The Road, for instance, isn’t just upset by the prospect of having to turn to canibalism himself; he’s sad that he and his father weren’t able to help the other people they found locked in the cellar.
We can’t help feeling strong positive emotions toward altruists. Katniss wins over readers and viewers the moment she volunteers to serve as tribute in place of her younger sister, whose name was picked in the lottery. What’s interesting, though, is that at several points in the story Katniss actually does engage in purely rational strategizing. She doesn’t attempt to help Peeta for a long time after she finds out he’s been wounded trying to protect her—why would she when they’re only going to have to fight each other in later rounds? But when it really comes down to it, when it really matters most, both Katniss and Peeta demonstrate that they’re willing to protect one another even at a cost to themselves.
The birth of humanity occurred, somewhat figuratively, when people refused to play the game of me versus you and determined instead to play us versus them. Humans don’t like zero-sum games, and whenever possible they try to change to the rules so there can be more than one winner. To do that, though, they have to make it clear that they would rather die than betray their teammates. In The Road, the father and his son continue to carry the fire, and in The Hunger Games Peeta gets his chance to show he’d rather die than be turned into a monster. By the end of the story, it’s really no surprise what Katniss choses to do either. Saving her sister may not have been purely altruistic from a genetic standpoint. But Peeta isn’t related to her, nor is he her only—or even her most eligible—suitor. Still, her moments of cold strategizing notwithstanding, we've had her picked as an altruist all along.
Of course, humanity may have begun with the sense that it’s us versus them, but as it’s matured the us has grown to encompass an ever wider assortment of people and the them has receded to include more and more circumscribed groups of evil-doers. Unfortunately, there are still all too many people who are overly eager to treat unfamiliar groups as rival tribes, and all too many people who believe that the best governing principle for society is competition—the war of all against all. Altruism is one of the main hallmarks of humanity, and yet some people are simply more altruistic than others. Let’s just hope that it doesn’t come down to us versus them…again.
Also read
And:

